Downloads
Keywords:
Toward Smart Bone Healing: A Review of In Vivo Evidence and Translational Perspectives on Bioelectronic Scaffolds and Piezoelectric Biomaterials
Authors
Abstract
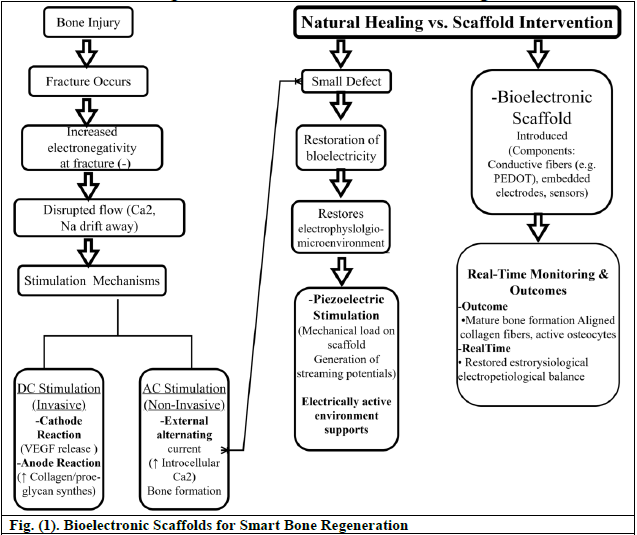
The limited self-healing capacity of bone and the disadvantages of traditional grafting methods make large bone defects a significant challenge in regenerative medicine. Recent developments in bone tissue engineering (BTE) have highlighted the therapeutic potential of bioelectronic scaffolds as well as piezoelectric biomaterials. As a result of these smart systems, bone regeneration can be actively controlled by responding to external or internal biophysical cues, including electrical and mechanical stimulation. A critical examination of recent in vivo studies using piezoelectric ceramics and polymers is presented in this review that explores the role of endogenous bioelectric signaling in bone healing. Furthermore, this study assesses the interaction between conductive scaffolds, electrical stimulation modalities, and piezo-responsive materials to improve osteogenesis, osseointegration, and vascularization. A particular emphasis is placed on translational implications, scaffold fabrication techniques such as 3D printing, and the integration of remote-controlled stimulation systems for battery-free and self-sufficient stimulation. The insights provided here provide a roadmap for developing next-generation bioelectronic platforms that can overcome current clinical limitations in orthopedic repair
Article Details
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

