Downloads
Keywords:
Efficient Gait Recognition Using a CNN-LSTM Framework Optimized with Hippopotamus Algorithm
Authors
Abstract
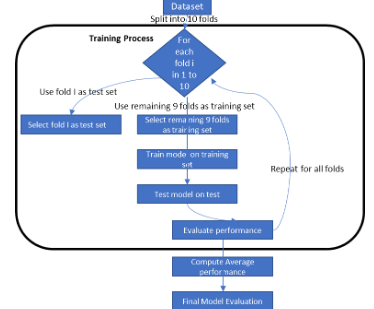
Gait recognition has emerged as a vital biometric technique for unobtrusive human identification in surveillance, healthcare, and behavioral analytics. However, achieving high accuracy under real-world variations such as walking speed, clothing, and viewpoint changes remains a significant challenge. This study proposes an advanced gait recognition framework that combines a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for spatial feature extraction with a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network for modeling temporal dynamics. To address the limitations of manual hyperparameter tuning, the Hippopotamus Optimization Algorithm (HOA); a bio-inspired metaheuristic is integrated to optimize key parameters such as learning rate, filter size, LSTM units, and dropout rate. The model is evaluated on the TUM GAID dataset, encompassing diverse gait variations. Experimental results demonstrate that the HOA-optimized CNN-LSTM architecture significantly outperforms baseline and state-of-the-art methods in terms of recognition accuracy, Genuine Acceptance Rate (GAR), and Equal Error Rate (EER). The proposed framework exhibits superior robustness and convergence speed, affirming the efficacy of metaheuristic-driven optimization in deep learning-based gait recognition systems.
Article Details
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

