Downloads
Keywords:
Real-Time Object Detection in Adverse Weather Conditions Using Transformer-Based Architectures
Authors
Abstract
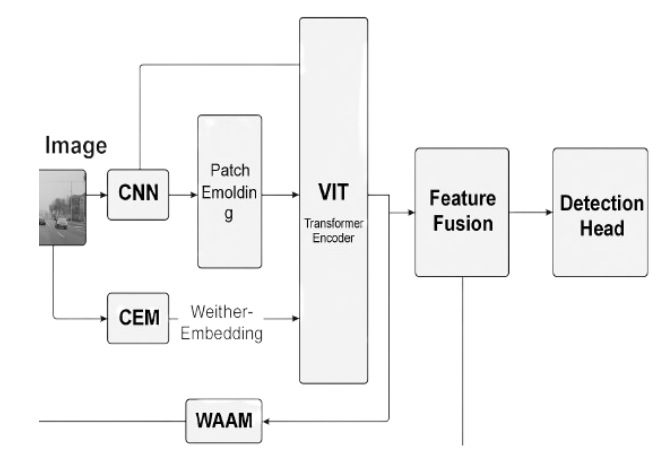
Real-time object detection has seen tremendous advances in recent years, driven largely by the power of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformer-based models. However, existing approaches still struggle to maintain detection accuracy under adverse weather conditions such as fog, rain, and nighttime low-light scenarios. These environments are critical for applications such as autonomous driving, aerial surveillance, and smart city infrastructure. This paper presents a robust transformer-based object detection framework designed to operate efficiently in challenging weather conditions without sacrificing real-time performance. The proposed system builds upon Vision Transformers (ViTs) and hybrid CNN-ViT architectures to capture both local texture and global context features. A novel weather-adaptive attention mechanism is introduced, enabling the model to dynamically reweight features based on visual degradation cues caused by environmental interference. We train and evaluate our framework using three leading weather-specific benchmark datasets: DAWN, Foggy Cityscapes, and NightOwls. These datasets encompass diverse visibility conditions, object categories, and urban scene complexities.
To ensure deployment feasibility in real-world systems, we incorporate lightweight architectural modifications, including quantization-aware training, positional encoding reduction, and pruning strategies. These optimizations significantly reduce model size and computational demand without compromising accuracy. Empirical results show that our model achieves real-time inference speeds of 25 to 30 FPS on edge-level NVIDIA Jetson devices, while improving mean Average Precision (mAP) by 10 to 14 percent under extreme weather conditions when compared to traditional CNN-based detectors such as YOLOv5 and Faster R-CNN. Additionally, ablation studies confirm the efficacy of hybrid backbones and weather-attentive feature fusion in handling occlusions, motion blur, and varying light intensities. This research offers a practical and scalable solution to a critical gap in robust computer vision, enabling safer and more reliable deployment in autonomous navigation and intelligent traffic systems that operate in non-ideal conditions.
Article Details
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

